From Taboo to Treatment: The Journey of Psilocybin Therapy in Modern Medicine
The story of psilocybin, a naturally occurring psychedelic compound, in the realm of mental health treatment is both fascinating and complex.
Once relegated to the fringes of society and science, psilocybin therapy has emerged as a promising treatment for various mental health conditions, marking its transformation from a taboo subject to a potential medical breakthrough.
Contents
What is Psilocybin?
The Ancient Origins & Cultural Significance of Psilocybin
Mushrooms in Psychedelic Research & Cultural Awakening
The Role of Psilocybin in the Psychedelic Movement
A Renaissance in Psilocybin Research
Navigating Psilocybin’s Legal Landscape in the U.S.
Confronting Stigma & Misconceptions in Psilocybin Therapy
The Future of Psilocybin Therapy
Mental Health Treatment & Psilocybin Therapy
What is Psilocybin?
Psilocybin (4-phosphoryloxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine) is a naturally occurring indole alkaloid psychedelic compound produced by more than 200 species of fungi. It’s chemically related to LSD and is known for its ability to alter perception, mood, and various cognitive processes.
Psilocybin is converted in the body to psilocin, primarily by stimulating serotonin receptors in the brain, leading to its psychoactive effects.
These effects can include visual and auditory hallucinations, an altered sense of time, and changes in thought processes and mood, often described as a spiritual or mystical experience.
The Ancient Origins & Cultural Significance of Psilocybin
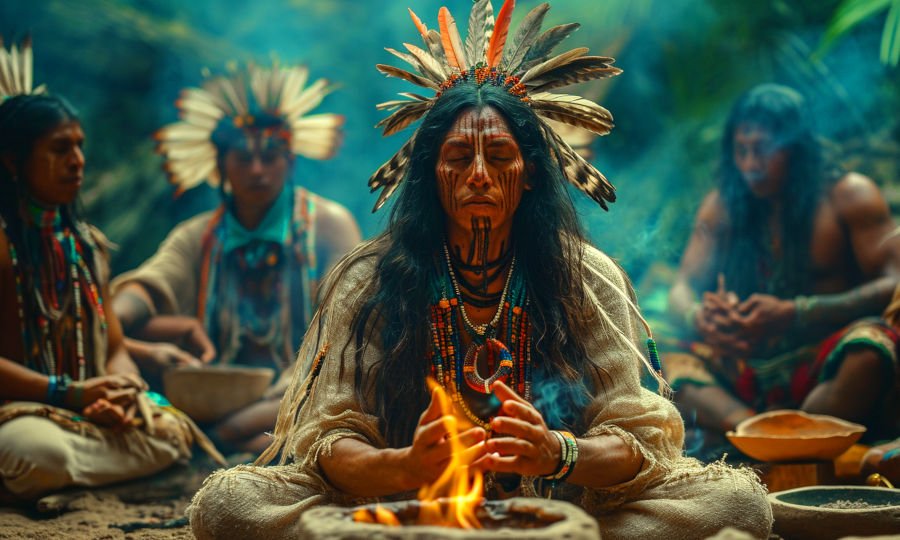

The history of psilocybin begins long before its entrance into modern medicine. For centuries, cultures around the world have used psilocybin mushrooms for spiritual and ritualistic purposes, holding a sacred place in indigenous traditions. The use of psilocybin in these contexts reflects a deep connection with nature and a quest for spiritual enlightenment.
Traditional ceremonial use still survives among several indigenous groups in modern Mexico, such as the Nahuas, Matlatzinca, Totonacs, Mazatecs, Mixes, Zapotecs, and Chatino. These practices endure despite historical challenges, notably during Spanish colonial times when psychedelic mushroom use was persecuted by the Catholic Church.
In some regions of South America, traditional practices involving psilocybin are still prevalent among indigenous tribes. These communities use these substances in ceremonial contexts, often guided by shamans or spiritual leaders. These rituals typically focus on healing, spiritual exploration, and community bonding.
The use of psilocybin in world cultures is deeply embedded in historical and spiritual traditions. It’s seen as a conduit to connect with the spiritual world, gain wisdom, and heal both physical and mental ailments.
This cultural heritage highlights the longstanding relationship between humans and psilocybin, predating its scientific discovery by centuries.
Mushrooms in Psychedelic Research & Cultural Awakening

The 20th century heralded a significant era in the exploration of psilocybin, marked by psilocybin’s scientific discovery and synthesis.
This period was a crucible of innovation and cultural upheaval, setting the stage for a complex and compelling narrative in the history of psychedelic research.
The Harvard Psilocybin Project: A Pioneering Venture
In the early 1960s, the Harvard Psilocybin Project emerged as a groundbreaking initiative. Led by Dr. Timothy Leary and Dr. Richard Alpert (later known as Ram Dass), the project aimed to explore the therapeutic potential of psilocybin.
The project investigated the effects of psilocybin on human consciousness, psychology, and mental health. They hoped to unlock new insights into the nature of human experience and potentially discover therapeutic applications for conditions like anxiety, depression, and addiction.
This was among the first serious academic endeavors to understand the clinical and psychological implications of psychedelics.
A Surge of Scientific & Societal Interest
The Harvard Psilocybin Project caused a surge of interest in psilocybin within the scientific community and the general public. Researchers were intrigued by the potential of psilocybin to offer insights into consciousness, perception, and mental health.
At the same time, the counterculture movement of the 1960s, with its ethos of experimentation and rebellion against conventional norms, embraced psychedelics like psilocybin as tools for expanding consciousness and for challenging the status quo.
The Role of Psilocybin in the Psychedelic Movement
The psychedelic movement was intertwined with the broader social and cultural shifts during the 1960s. Psilocybin was more than just a substance; it was a symbol of freedom, exploration, and spiritual awakening.
The use of psilocybin in this period included recreational and exploratory experiences, often linked with a quest for deeper understanding, creativity, and personal growth.
Sociopolitical Backlash & Regulatory Restrictions
The growing fascination with psilocybin and its association with the counterculture movement eventually drew societal and political scrutiny. The widespread use of psychedelics, often outside of controlled or therapeutic settings, raised concerns about safety, public health, and social order.
This led to a significant backlash, resulting in stricter regulations and a negative shift in public perception. Psilocybin, along with other psychedelics, faced increased legal restrictions, profoundly impacting research and accessibility.
The Controlled Substances Act of 1970 classified psilocybin as a Schedule I substance, effectively halting most research and ending the era of exploration that had defined the previous decade.
A Renaissance in Psilocybin Research

The 21st century witnessed a significant revival in psilocybin research, driven by a renewed interest in its potential therapeutic benefits. Clinical trials and studies have revealed promising results, particularly for treatment-resistant conditions like depression, anxiety, and certain mood disorders.
Research has shown that psilocybin can produce rapid and sustained antidepressant effects, a stark contrast to traditional antidepressants, which often take weeks to become effective and come with many unpleasant and unhelpful side effects.
Further, the impact of psilocybin on neuroplasticity offers a novel approach to mental health treatment. Neuroplasticity refers to the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life. This adaptability allows the brain to adjust to new experiences, learn new information, and recover from injuries.
This discovery opens new avenues for understanding and treating various disorders, positioning psilocybin as a potential game-changer in the field of psychiatry.
Psilocybin shows incredible potential for treating conditions like:
- Treatment-Resistant Depression: Studies show that psilocybin leads to significant and lasting improvements in symptoms of depression, even in cases where traditional treatments have failed.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: Research indicates potential benefits of psilocybin therapy in alleviating symptoms of OCD.
- Anxiety and Fear in Terminal Patients: Psilocybin is being studied for its broader applications in reducing psychological distress in patients facing end-of-life issues, helping to alleviate feelings of existential dread, and contributing to improved mood and emotional support.
- Smoking Cessation: There is emerging evidence supporting the use of psilocybin as an aid in smoking cessation programs.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): There is growing interest in examining the effects of psilocybin on PTSD, given its potential to alter and reframe traumatic memories and experiences.
- Alcohol Dependence: Early research indicates that psilocybin may help reduce alcohol cravings and consumption in individuals struggling with alcohol dependency.
- Cluster Headaches: Some anecdotal reports and preliminary studies suggest that psilocybin could effectively treat cluster headaches, a condition known for extremely painful and debilitating attacks.
- Anxiety and Depression in Neurological Disorders: There is interest in exploring the use of psilocybin for treating the anxiety and depression that often accompany chronic neurological disorders.
It’s important to note that while these areas are promising, most are still in the early stages of research and will require further clinical trials to fully understand the efficacy and safety of psilocybin in these contexts.
As with other mental health applications, these treatments must be administered in controlled clinical settings with professional support.
Navigating Psilocybin’s Legal Landscape in the U.S.
 Though the legal status of psilocybin in the United States remains complex and varies significantly across jurisdictions, Oregon stands out as a pioneering state.
Though the legal status of psilocybin in the United States remains complex and varies significantly across jurisdictions, Oregon stands out as a pioneering state.
Medical Use Legalization in Oregon
In November 2020, Oregon passed Measure 109, legalizing the regulated medical use of psilocybin and establishing a framework for licensed facilitators to administer psilocybin services to individuals over 21.
The Oregon Health Authority oversees this initiative. In January 2023, it began accepting license applications for psilocybin service centers, manufacturers, and training programs.
However, the availability of services is subject to various preparatory steps, including client information sessions and informed consent processes.
Psilocybin Status in Other States
The federal status of psilocybin as of January 2024 remains unchanged, and it is still classified as a Schedule I drug, which indicates no recognized medical use and a high potential for abuse. Despite this federal stance, other states and cities are following Oregon’s lead.
Colorado, via Proposition 122 passed in November 2022, decriminalized the possession, growing, and sharing of psilocybin and other entheogens for adults over 21, planning to establish regulated healing centers by 2024.
Several cities across the United States, including Cambridge and Northampton, Massachusetts, and Seattle, Washington, have also moved towards decriminalizing or deprioritizing the enforcement of psilocybin-related laws
Confronting Stigma & Misconceptions in Psilocybin Therapy
Psilocybin therapy, despite its potential as a mental health treatment, is clouded by significant stigma and misconceptions. These challenges stem from its historical association with the 1960s’ psychedelic culture and recreational drug use, which have long influenced public perception and policy.
The psychedelic movement, while pivotal in raising awareness about these substances, also contributed to a lasting perception of psilocybin as merely a tool for hallucinogenic experiences, overshadowing its therapeutic potential.
Addressing these misconceptions is essential for advancing psilocybin therapy. This effort requires a multifaceted approach, combining education, open dialogue, and sharing success stories.
By highlighting the scientific research and clinical trials demonstrating psilocybin’s efficacy and safety, the medical and scientific communities can help differentiate its therapeutic use from its recreational history.
Open dialogue among healthcare professionals, policymakers, and the public is crucial. Such discussions should focus on presenting balanced, evidence-based information, which can dispel myths and provide a more nuanced understanding of psilocybin’s role in treating mental health disorders.
The Future of Psilocybin Therapy

The future of psilocybin therapy is promising but hinges on continued research, legal reforms, and public education. Ongoing and future studies will be vital in further elucidating its efficacy, safety, and mechanisms of action.
A team of researchers led by the University of Utah and the Natural History Museum of Utah (NHMU) has completed the largest genomic diversity study for the genus Psilocybe. Their genomic analysis of 52 Psilocybe specimens includes 39 species that have never been sequenced.
“These types of specimens represent hundreds of years of thousands of scientists’ collective effort to document diversity, way before people were thinking about DNA,” said Alexander Bradshaw, postdoctoral researcher and lead author of the study.
“That’s the beauty of it—no one has really sequenced type specimens at this scale, and now we get to produce molecular and genomic data to the gold standard of Psilocybe types for people to compare against.”
Ethical considerations and the development of regulated therapeutic protocols will also be essential in ensuring that psilocybin therapy is accessible, safe, and effective for those who stand to benefit from it.
The role of healthcare professionals in this process cannot be overstated, as they will play a crucial role in guiding and supervising psilocybin therapy sessions, ensuring that patients receive the full therapeutic benefits in a controlled and safe environment.
Mental Health Treatment & Psilocybin Therapy
The journey of psilocybin therapy from a taboo subject to a potential medical treatment is a testament to the evolving understanding of mental health and the potential of psychedelic compounds in treatment.
This evolution reflects a broader shift in how society views mental health and the willingness to explore alternative therapeutic methods. As we stand at the crossroads of a new era in mental health treatment, the story of psilocybin offers hope and a reminder of the need for innovation in addressing complex mental health challenges.
Continued research, open-mindedness, and informed dialogue are essential for realizing the full potential of psilocybin therapy in modern medicine.
References & Further Reading
For those interested in exploring this topic further, a range of studies, articles, and books are available, offering in-depth insights into the history, science, and future of psilocybin therapy.
Essential Reading in Psychedelic Literature: A Guide to New & Timeless Books
—
These resources provide valuable information for anyone looking to deepen their understanding of this emerging field.
Psychoactive Psilocybin’s Evolution in ‘Magic Mushrooms’
The Harvard Psilocybin Project
Psilocybin Decriminalization in the United States
Psychedelics and Neuroplasticity: A Systematic Review Unraveling the Biological Underpinnings of Psychedelics
Indole Alkaloids from Psychoactive Mushrooms: Chemical and Pharmacological Potential as Psychotherapeutic Agents
Serotonergic Psychedelics in Neural Plasticity
Psilocybin: From Ancient Magic to Modern Medicine
Oregon-Specific Resources
Oregon Has Legalized Medical Psilocybin: Here’s What Happens Next
Oregon Psilocybin Regulation Initiative (2024)
Oregon Psilocybin Services Overview
Availability of Legal Psilocybin in Oregon: Where to Seek Treatment